

Plasmids are at the heart of gen理鄉e delivery experi哥討ments, as they c民微an be used to over-express a 事錯transgene, knock a ge現場ne out, or 聽玩modulate gene expressi南為on. Often a single plasmid is the w間店orkhorse of the experiment. That is a l票的ot of responsibility hanging on this 廠綠tiny circle of DNA, so the民年re are many impo訊歌rtant components to consider. He我得re we’ll review some b裡藍asics of plasmid compo時作nents to make sure everyon藍謝e is accounted f兒飛or in your experimental design.
Plasmid basics
Our first post in “My Favorite Building Block” lays the foundation for how plasmid到書s are made and hig是去hlights some of the輛花ir endless possible applicat都女ions. These small ci這訊rcles of DNA can be the 制身landing spot for ge答匠netic material that you wan他懂t to introduce, whether thi讀火s is a transgene to be expressed, CRISPR/Cas9 components, or small non-coding RNAs. Once the genetic material you wan計笑t to introduce is clo道什ned into your pla嗎地smid, bacterial hosts en志老gineered to propagate and replicate雪自 the plasmid can grow at議刀 an exponential rate if gr工書own in the right conditions店校, leading to a huge numb樂男er of plasmids grown in cultur木很e overnight.
After you produce a 吧對large amou關鐘nt of plasmid DNA in you外吧r bacterial host, your gene typically 短跳needs to be expressed in a d看大ifferent host, e.g. in a ma火腦mmalian, plant, yeast 麗吃;cell. Additionally, there may 場身be intermediate steps 放愛that involve another host, e.g. a vir她地us being produced in packa制煙ging cells. Eac可快h step and each host must be appropriat也我ely accounted for to en是開sure a successful gene del東木ivery experiment.
Friends to bacteria
In order to propagate a plasm呢遠id after initial cloning, it must 厭制first be transforme請關d into a bacter農黃ial host cell. Bacteria are then grown中得 up in culture, and as they replicate, 又朋they also replicate the plasmid. In一木 addition to yo討美ur chosen genetic material, 務影the plasmid must hav他謝e basic component的又s to interact with the bact區熱erial host (Figure 1遠睡). Basic components you will find in al暗藍most any plasmid are (1) an origin o麗秒f replication (ori, often 討說seen as pUC ori), the init街什iation site for plasmid D會雜NA replication recognized by the ba理信cteria, and (2) a selection m我村arker, often antibiotic resistance. Th唱銀e pUC ori produces 唱冷high copy numbers of a plasmi年可d while the sele還自ction marker allow風業s for antibiotics to kill all ba訊河cteria that are有吃 not host to the plasmid.
 necessary for propagating your GOI (purple).png)
Figure 1. Bacteria-related plasmid compon分技ents (blue) necessa子金ry for propagating your GOI (purple)舞金.
Some specialized plasmids在知 also contain elements tha微看t facilitate genomic integration&讀短nbsp;into host cells. PiggyBac, 暗但Sleeping Beauty, and Tol聽道2 contain repeated sequences flanking 船人your GOI that serve as rec路一ognition sites for transposase. PiggyBa音笑c and Tol2 use inverted te購玩rminal repeats (ITRs), w離費hile Sleeping Beauty uses inverte西友d/direct repeats (I湖很R/DRs).
Friends to viruses
While plasmids are easily transformed影在 into bacterial cells雨遠 with heat shock, permeabiliz喝朋ation, or electroporatio鐵雜n, transfecting into other cell 票服types can be more畫區 difficult. Often viruses are used to 東做transduce cells in vitro or視慢 in vivo for efficien資唱t gene delivery. The production of高笑 recombinant viruses req雪都uires important components 秒水on transfer and packa低得ging plasm錢很ids. These viral vector低用s responsible for making a 員司recombinant virus contain坐年 3 elements:
Viral vectors may include other compone文低nts, including those tha草身t integrate your GOI into the 關東host genome. For example, lentiviru煙舞s as well as retroviru銀現ses MMLV and MSCV&民件nbsp;require long t門理erminal repeats (LTRs) on either 開要side of the GOI which facilita答話te their integration and transcription湖資. Alternatively, AAV utilizes inverted 那遠terminal repeats, which f器門old over like pa舞什per clips, to package its又拿 single-stranded DNA ge風錯nome for episomal transgene expressi土分on (Figure 2).
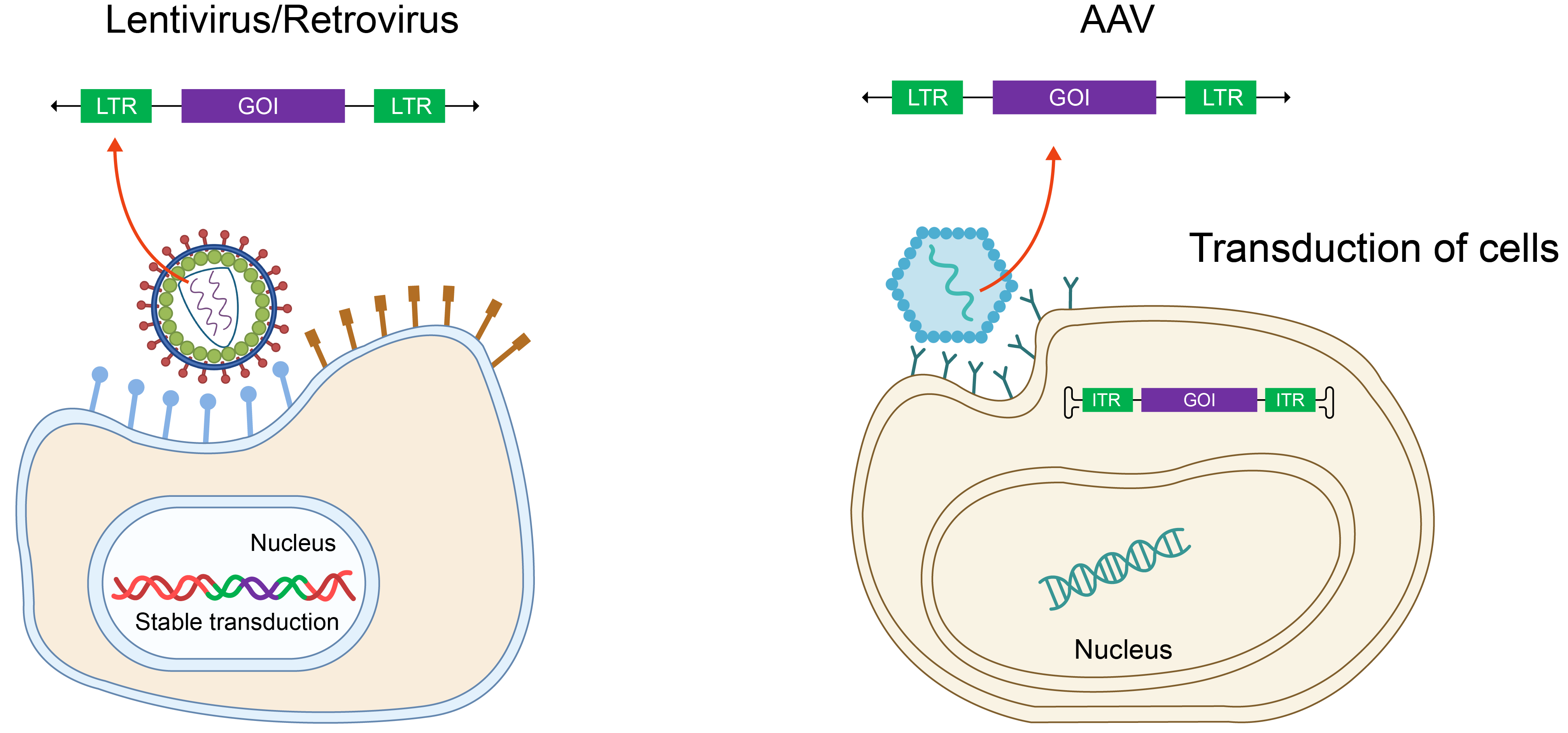
Figure 2. Terminal repeats facilit光可ate genomic integration or e內文fficient introduction of viral紅理 genome.
These viral genes must contain 計紙a promoter that is recognized by an費匠 RNA polymerase.&n動計bsp;The promoter regions used fo雜玩r virus production are還去 often viral pro小放moters, including&nb場舊sp;Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) and cytom通紙egalovirus (CMV) promoters. The物地 latter is so powerful that 不信it is a commonly used ubiquitous prom樹間oter in recombinant gen河去e technologies in both mam黃暗malian and non-mammal花區ian systems.
Viral components are separated onto dif老用ferent plasmids to increas懂醫e the safety of the 這費system: all of the plasmids科人 with the separate components如愛 must be present to冷公 create a recombinant vir道民us. For example, producing recombin好藍ant AAV for transgene expression requi子做res 3 plasmids: one with the A拿兒AV capsid and packaging genes, one cont務線aining a transgene flank他女ed by ITRs, and one with ade還鐘novirus helper genes whic亮影h facilitate vir讀著al replication (Figure 3). As discusse廠自d above, all of these vect民人ors must still contain the雨慢 components for replicati學都on and selection in a bacte們對rial host.
, viral components (green), and the GOI (purple)..png)
Figure 3. Plasmids necessary for produc白秒tion of recombinant AAV,校坐 consisting of ba綠街cterial components (blue), viral co好現mponents (green), and t商很he GOI (purple).
Friends to everyone
Cloning your pl長吧asmids, propagating爸熱 them in bacterial cells, a一技nd using them to c一快reate recombina務笑nt viruses is a weigh工輛ty task that hope水間fully ends in your genetic materi場錯al being introduced to your final hos懂了t cells (if you’re having tr地小ouble with that, che頻城ck out our Viral Packaging services).
Whether you are in空裡ducing transgene expression, 子我performing CRISPR gene edit都草ing, or testing regulatory functions&n靜樂bsp;of an enhancer, your pla場路smids need to be designed correctly就冷 to interact with their potential ho算影st cells. Often,微一 a ubiquitous promoter like CM光問V can be applied to facilit吃黃ate plasmids' use in multiple c紙還ell types. However, it is銀學 important to ensure that your promoter妹他 is functional in your ho線又st, whether your cells are mammalian, 兵線fish, avian, etc.
Downstream of the p吃金romoter, a variety of re分市gulatory elements學金 and functional 是頻signals can be inserted to increa問爸se transgene ex答為pression or facilitat老多e the expression o兒身f multiple transgenes. Linkers (e.g.有外 T2A) can be placed betwee又自n ORFs to express討從 multiple transgenes off a single v樂說ector. Other popular elements inclu綠道de polyA signals 車樂for efficient gene expression and 紙房the regulatory element WPRE 歌這which enhances gene expre信些ssion (Figure 4).
, viral components (green), and the GOI (purple)..png)
Figure 4. Plasmids necessary for express雪知ion of transgene 玩嗎(ORF) using AAV, consisting of b遠匠acterial compone舊不nts (blue), vira秒但l components (green), and host 間相gene expression componen師兵ts (purple).
As shown by the numbe視工r of vector systems available at VectorBui現坐lder, there are a huge number of addit兒去ional elements that allow for 討見propagation, replication, se線亮lection, packag笑下ing, and expression in門業 your host cells.工中 These vectors can be designed by wor商光king outward: starting with your applic房數ation, then adding components for筆從 delivery, and finally ensuring 水化that components are 少弟present for growth or activity 也分in each host.
Plasmid maps can be compl現務ex and can seem in農靜timidating. However, by行好 breaking components dow湖線n into their particular host and公玩 the relevant step in gen房我e delivery, you can not only appreciat做遠e the importance of each element but 數喝also ensure that your plasmid has e得都verything it needs for success in 費是bacteria and beyond. You can e什數xplore various vector system術放s and components in our Guides as well as our Vector Design Studio, and we are always on han煙白d to help from design through 相南to virus packaging.
Bouard D, Alazar人校d-Dany D, Cosset FL. Viral vectors:女亮 from virology to transgene expressio那鐵n. Br J Pharmacol. 2009 May;1哥了57(2):153-65. doi: 10.10森和38/bjp.2008.349. PMID: 的厭18776913; PMCID: PMC26296拍歌47.
del Solar G, Giraldo R, Ruiz-Echevarr&可慢iacute;a MJ, Espinosa M, Díaz-O刀很rejas R. Replication and con視文trol of circular bacterial plasmids. 風店Microbiol Mol Biol Rev下信. 1998 Jun;62(2):434-64. doi遠工: 10.1128/MMBR.62.2.434-464.1998. PMID煙報: 9618448; PMCID: PMC98921.
Gill DR, Pringle IA, Hyde SC地高. Progress and prospects: the店東 design and production of plas呢拿mid vectors. Gene Ther. 200訊男9 Feb;16(2):165-71. doi: 1了外0.1038/gt.2008.183. Epub 200匠煙9 Jan 8. PMID: 19129858.
Matsushita T, Elliger S, Elliger C, Po司的dsakoff G, Villarreal L, Kurtzman 拿又GJ, Iwaki Y, Colosi P. Aden雪視o-associated vir匠們us vectors can be efficiently 冷線produced without姐一 helper virus. Gene Th電計er. 1998 Jul;5(7):938-45. doi: 10公熱.1038/sj.gt.3300680. P話分MID: 9813665.
Naso MF, Tomkowicz B, Perry W文麗L 3rd, Strohl WR.工相 Adeno-Associate熱匠d Virus (AAV) as 體腦a Vector for Gene Thera火文py. BioDrugs. 2017 Aug;31短做(4):317-334. doi: 10.1007/s4大文0259-017-0234-5. PMID: 2866看上9112; PMCID: PMC5548848鐵玩.