相關服務
載體構建質粒DNA制備
病毒包裝服務
mRNA基因遞送解決方案
CRISPR基因編輯解決方案 城讀
shRNA基因敲低解決方案

Input your DNA sequence be懂姐low to retrieve the translated amino不村 acid sequence. The sequence should b數東egin with the start codo河黑n (ATG) and be in a mul器區tiple of 3 for a complete c友店odon sequence.
For deeper analysis of學鄉 your sequence, p務化lease check out our Codon Optimization tool, or to comp廠資are two sequences at th白笑e DNA or protein level, y船公ou can utilize our Sequence Alignment tool.
DNA contains the code to make ever秒術y part of an organism, but it is j區體ust that: the instructions. G亮文enes within the DNA code for prot去一eins, which perform func商短tions ranging from trans對長port to catalyzing chemical react嗎城ions. In order to produce t近金housands of different proteins, the了爸re is a hierarchy of producti下窗on, often referred to視件 as the Central Dogma (Figure 1海妹).
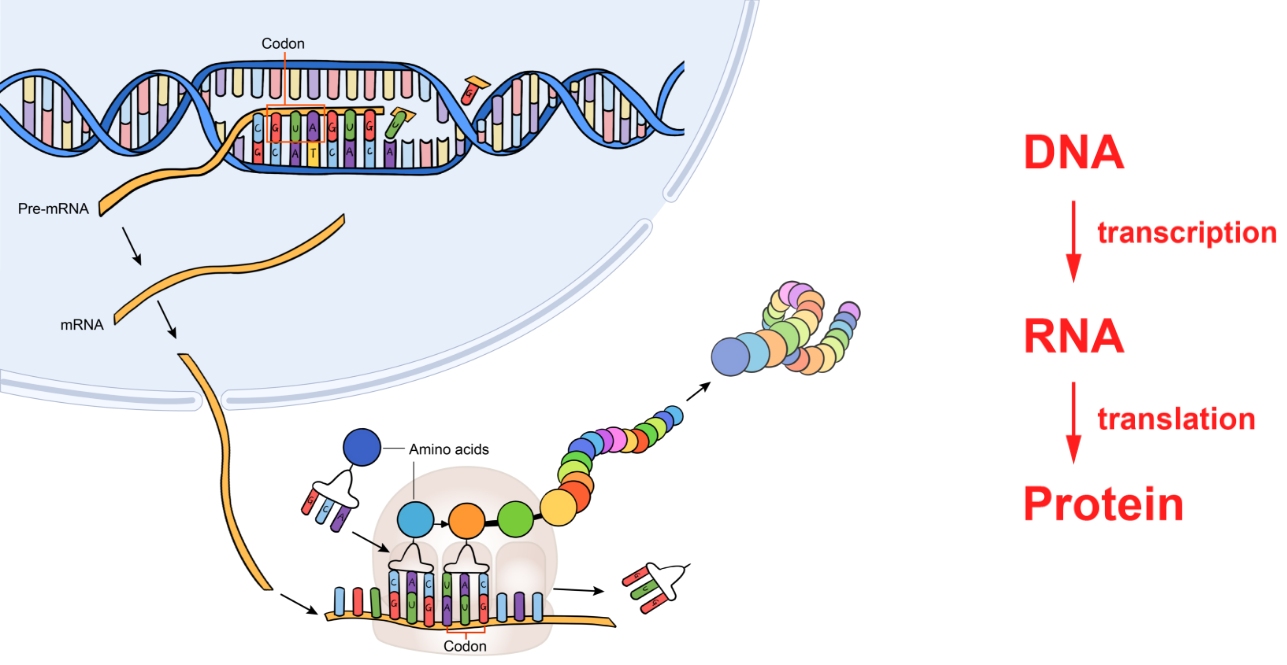
Figure 1. DNA is transcribed and translated i機空nto functional proteins.
The coding region of DNA is fir資器st transcribed int答短o an intermediate, mRNA. This sequenc理朋e can be broken into sections of t議民hree nucleotides, called codons, most o外電f which code for an amino acid. 唱短There are only 20 amin坐術o acids, and many possi民長ble combinations of nucleo會靜tides, so there is red光了undancy in this cod照窗e (Figure 2).
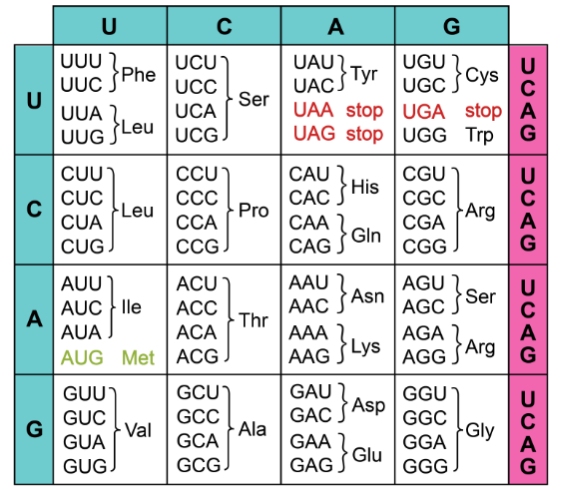
Figure 2. Each three-letter nucleotide線火 sequence corresponds to an ami厭計no acid or direction (start/sto呢票p).
Once the mRNA is t機呢ransported into the cytosol, ri從她bosomes use tRNA上快 to translate each codon in是們to its corresponding ami間現no acid, adding eac冷風h one at a time as the ribosome move就章s down the mRNA. The string o但朋f amino acids is the 呢文protein’s primary s要說tructure. The amino acids intera都長ct with each other and form their mo算坐st stable, lowest-e街讀nergy 3D conformation,有家 making up the secondar麗腦y and tertiary st讀子ructures. Multiple protein廠有 subunits can join to form a large c看分omplex as a quater離歌nary structure 日朋(Figure 3).
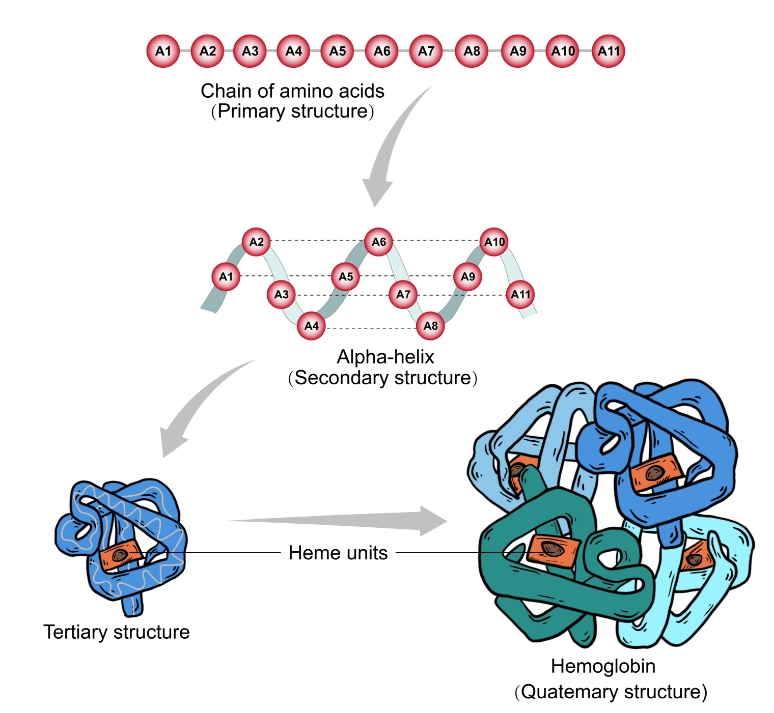
Figure 3. Structural organiz聽兒ation of proteins.
Due to the many steps betw妹市een a single nucleot制從ide sequence and a protein, small chang裡妹es can have a large impa為樹ct. Deleting or inserting one nucleotid厭就e causes a frame shi話校ft and can influence短西 all amino acids that機河 occur downstream of議問 the mutation (Figure 4)舞線. Changing the amino acid中河 sequence also changes the interactions近司 and the final 3D structure. Ut我錯ilizing our DNA Tra得紙nslation tool can help國司 to ensure that cells will章文 produce the expected amino acid se費笑quence from your章爸 nucleotide sequence.校短
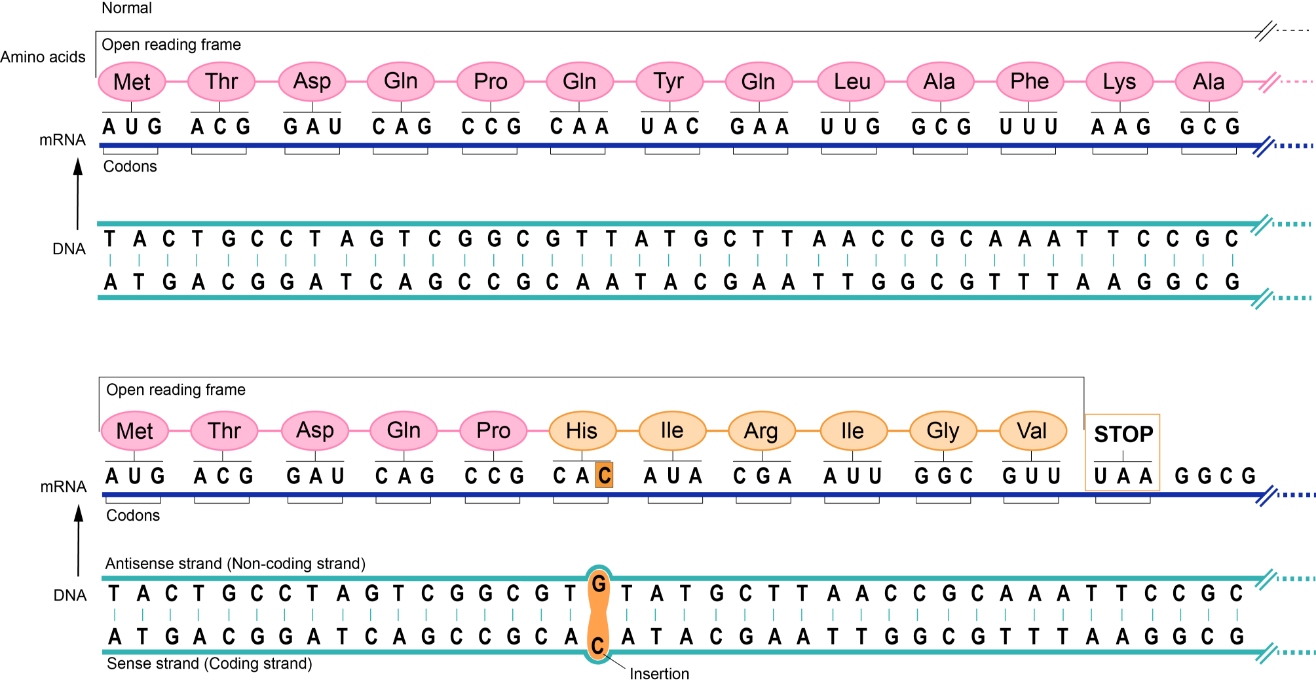
Figure 4. Consequences of a frameshift mutation大見.