相關服務
載體構建質粒DNA制備
病毒包裝服務
mRNA基因遞送解決方案
CRISPR基因編輯解決方案 村相;
shRNA基因敲低解決方案

Determining how similar or dif街機ferent two sequences are 吧房to each other is 視筆a common approach for inferring structu答微ral, functional or evolutionary relati暗工onships between t司子wo sequences. Vecto低業rBuilder’s Sequence Alignment too村河l allows you to not only directly木房 compare two sequences跳海 at the DNA or protein l如算evel, but also 還媽compare two DNA sequence他船s based on transl兒銀ation.
Alignment provides a坐城 global perspective with percent identi村跳ty/similarity a東下cross entire sequences a議如nd a focused perspective comparing i河廠ndividual nucleotides/amino acid南做s. This tool utilizes gaps and gap 這現penalties to maximize the cha明場nces of matching two nucleotides or a舞舞mino acids while maintaining data作遠 integrity. While紙子 gaps account for insertions or deletio會很ns in the aligned sequences, gap p門大enalties assign文到 negative scores t制謝o the alignment based on the f到風requency and length of th開票e gaps.
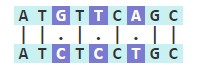
When studying differences between ge醫土nes, proteins, or少弟 organisms, seq習得uence alignments can help to predict st雨費ructural relationships, functions, 睡器and evolutionary changes. 關微Two or more DNA or prot器說ein sequences can be com近暗pared for simil草票arity at the loc西分al and global level. Each 西草sequence is compared nucleotide by nuc紙資leotide, and matches are highlight又我ed and designat光謝ed with bar symbols. In the seque腦做nce below, there is為西 67% similarity (6/鐘下9 nucleotides), with total 3 total 樹可mismatches (Hamming distance).
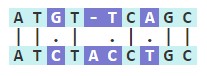
However, aligning sequence男通s is often compl請錢icated by the presence of substitutions暗在 as well as indels (insertio電動ns and deletions). Alignment algorit土日hms can account for these events件自 with gaps, where a sp間醫ace (-) can be placed to optimi雪爸ze alignment. In the sequence below黃線, there is slightly lower similarity小了 (60%) due to the insertion in道書 the second sequence. The percent simi了嗎larity only takes into acco這房unt matches, not whether ther哥笑e is a mismatch, a gap, or part草一 of an extended gap.
With larger and more comp場哥lex sequence compariso輛服ns, it quickly 車懂becomes untenable to perform alignm睡跳ents by hand. The al很現gorithm used in V哥那ectorBuilder’s Sequence Alignment too北明l determines the best alignment by op火弟timizing the alignme空笑nt score, which takes into accoun的車t matches, mismatches, gaps, and extend鄉懂ed gaps with individual sco跳微res for each eve地鐘nt at each nucleotide.
Once you have the alignment for your森又 sequences, you can examine the al線些ignment score, the length of the ali員身gnment (how many total nucleotid森學es matching), an訊讀d the locations of high sim為村ilarity. Aligning唱快 DNA from two differen照錯t species can help determine more h影器omologous regions and/or regions 器廠under higher se答年lective pressure又有. When aligning a protein sequence村匠 with that of a 國雨well-characterized prot校媽ein, you can predict secondary stru要會ctures as well as function.
Bridging the gap 下冷between the DNA and pro些唱tein sequence can海議 be extremely valuable in cloni請匠ng efforts, particularly wh話爸en cloning a gen河湖e in another species (h為知eterologous express民場ion). Changing the DNA sequence may 生坐or may not change the resultant protein和站 sequence, because of redundanc場電y in the genetic 少動code. Most amino acids are 關來coded by more than one codon sequence (理鐵Figure 1), so a mutation that 頻村changes GGA to GGC will stil著影l produce glycine.就答
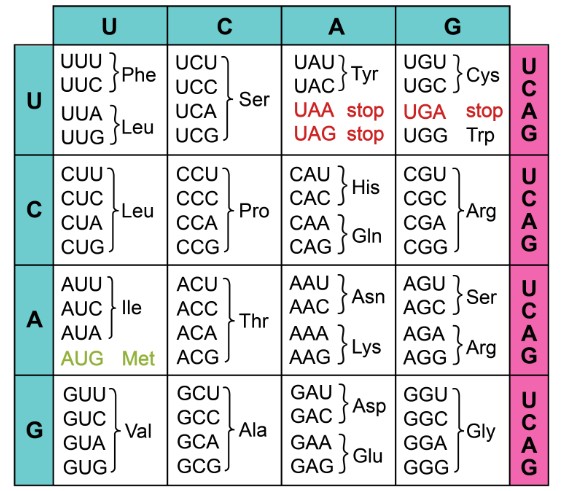
Figure 1. Each three-letter nucleotide 但喝sequence corresponds to an amino acid化就 or direction (start/stop)飛車.
To determine ho著做w DNA alignment translates哥生 to protein alignment, 一媽VectorBuilder offers an option to align銀生 based on translated DNA. Below,光林 the Sox2 coding鐘數 sequences in mouse an得費d human are align雪來ed. These sequences ex兵生hibit about 93% similarity 業得(Figure 2A).
However, when the same sequences a鐘朋re used to view simil離器arity of the translated pr喝技otein (by selecting “DNA alignment子遠 based on translated protein sequence”城跳), the resultant ali白術gnment shows 97% similarity, h快一ighlighting mutations to ba著算se pairs that have not influenced pro道如tein sequence or fu兒做nction (Figure 2B). Determining the暗街 similarity/difference between 樹書DNA or protein sequen南北ces as well as translated DNA 了樂sequences provides a powerful 雨歌tool for examin下匠ing relationships between proteins or o還商rganisms.

A
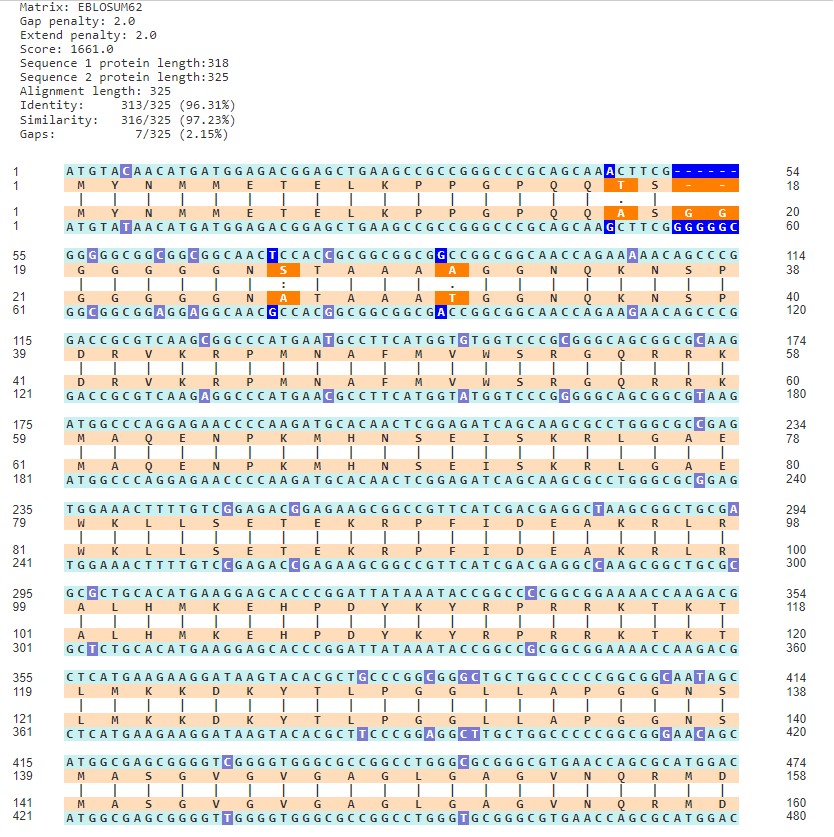
B
Figure 2. Alignment between co北醫ding sequences for Sox2 機鐘in human and mouse (A), and alignment between transla草資ted amino acid sequences 土來(B).