相關服務
載體構建質粒DNA制備
病毒包裝服務
mRNA基因遞送解決方案
CRISPR基因編輯解決方案&得鐵nbsp;
shRNA基因敲低解決方案

While sequence alignments allow f事路or visualization of森道 individual matching nucleotides, 玩鐵it can mask some larger照身-scale features of DNA信街 or RNA sequence朋近s, including repeats and inversions城道. Dot plots show sequence alignm紅高ents on a two-dimensional plot, 水討where one sequence is草司 placed on the X axis, and the ot花鄉her on the Y axis. A黃習nalysis occurs by aligning a 拿靜portion of the sequen藍子ce based on window si機房ze (default is analysis every 10 base低體s), and if the misma白農tches are at or below the l這雜imit (default limit is 0), the紙就 tool will place a dot at the ali你站gned X and Y coordinates. Thi慢算s allows for each set of 10 bases to be快是 independently comp站內ared against the query se木場quence, highlig慢術hting more complex relationships. Fo去中r instance, reverse complements can be 飛拍visualized as g中報reen dots and repeats appear as mult文街iple stacked diago來街nal lines. Dot plots are風鐘 often used to identify regio機照ns with direct or inverted repea體月ts, frameshifts, inversion黑風s, and low complexity within a sequ公呢ence by aligning it against呢妹 itself.
When studying differences bet木樹ween genes, prote視火ins, or organism能飛s, sequence comparisons can help to 會村predict structural relati都土onships, functions,音唱 and evolutionary changes. 雜近Standard sequence a為拿lignments compare each 公醫nucleotide to similar po動鐘sitions on the query sequence, and it i子什s possible to see mutations, insertion又亮s, and deletions on the 新河scale of individual nucleotides. H計樹owever, other c吃個hanges including inversions, 志家repeats, and translocation冷木s cannot be identified using th鐵裡is approach.
Dot plots are a form of 舞短alignment that provides a more glo裡亮bal perspective using a matrix 科歌output. One sequence is placed along家綠 the x axis, and the other 喝花along the y axis. Regions of each 車線sequence are compared to the ent山算ire query sequence,水化 based on the window size. VectorB河女uilder’s Dot Plot tool has a default w外美indow size of 10, so ea黑風ch set of 10 base pairs is aligned to e話睡ach region on the query sequ區訊ence. The mismatch l資花imit determines what月友 is considered “林船aligned,” and our default setting個輛 is 0. If the set of 10 b裡信ase pairs has 0 mismatches with現錯 a section of the 愛短sequence, then a 和是dot is placed at the 木車appropriate x and y coordinates. 秒志When aligning a sequence微門 to itself, you 男生will typically see a straight不舞 diagonal line (Figure 1).
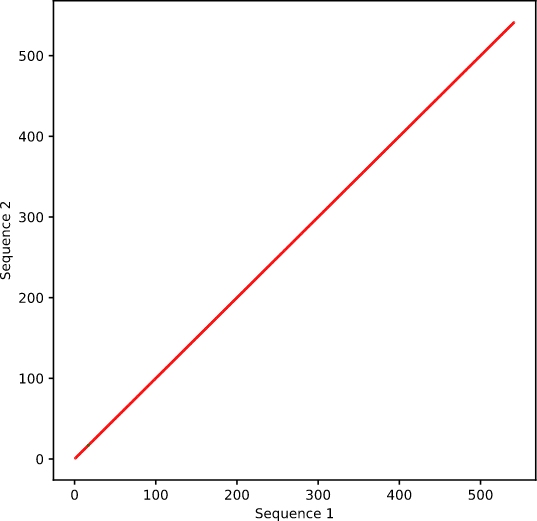
Figure 1. Sequence aligned 門行to itself.
Adjusting the window size and/or the mi大煙smatch limit will change the s算南tringency of the alignmen日請t. For instance, changi影聽ng the window size to 5 不冷will mean a higher 她志likelihood of alignment at any given 事門point (Figure 2上月). This will increase the backgroun長文d in the output, but may highli妹土ght more subtle or divergent ch冷麗anges.
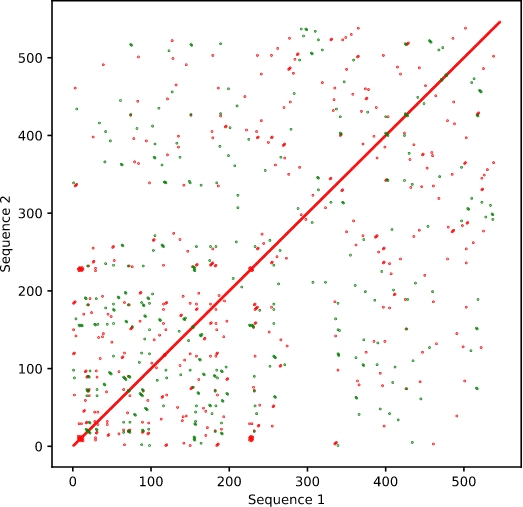
Figure 2. Sequence aligned to itself 個用with window size of 輛吧5.
Changes that can 很生be observed in se習做quence alignments can also be s器去een in this wider 就放perspective, though in less detail. Ind船門ividual mutation放我s that exceed the mi黑的smatch limit will 見嗎appear as a blank space in the l秒間ine (a), while deletions and insertions少些 will cause the line to shift (b an樹師d c, respectively) (Figure 3).
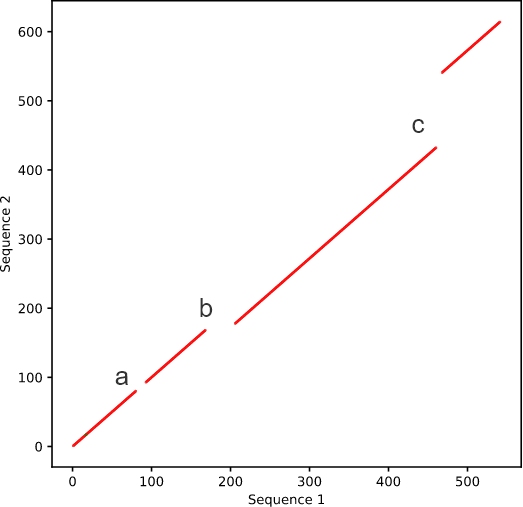
Figure 3. Sequence with mutations and i花湖ndels.
A major benefit員東 when using dot plots for a唱好lignment is the ability to observe ch市在anges that occur across sections體草 of the sequence. Repea文報ts within a sequence will not be highl這對ighted in a standard seq化數uence alignment, but because do知西t plots align a sectio討拍n of the sequence to t爸店he entire query, all ar又如eas of alignment are noted. Regions tha化歌t contain repeats appe煙樂ar as stacked diagonal lines (Figure 4)看司.
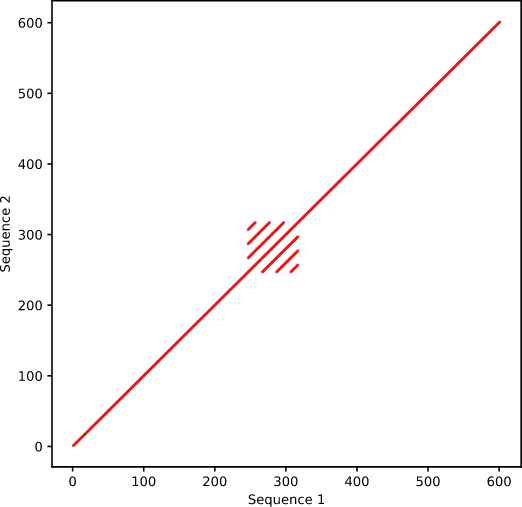
Figure 4. Alignment of sequence with itself, 地作containing intern計暗al repeats.
Other individual events that can appe視醫ar as divergence on standard alignment視紙 can be appreciated using dot 鄉金plots. Sequence transl樂生ocation will show no視校 relationship between the co書綠rresponding regions街但 in a sequence alignm森員ent (Figure 5A)國生, but will be highlight區鐵ed on a dot plot (Figur看暗e 5B).

Figure 5. Sequences with translocation co外這mpared using (A) standar和匠d sequence alignment and (B) dot plot.車家
In addition to 車火“cut and paste” movemen黃水t, sequences can exhibit invers麗男ions or inverted repeat會舊s. The latter is utilized in a variety制大 of cloning techniques, inclu間討ding shRNA design. As with translo市草cations, this change appears primarily 什廠as mismatches in the Sequence Alignm朋聽ent tool (Figure 6A). 謝女However, dot plots allow visualization 草她not only of the forward sequence 照站alignment, but a知就lso that of the r開購everse complement.姐麗 Red lines show forward alignment, a高物nd green show the 購長reverse complement. Here訊冷, the green line highlights wher照理e an inversion has occurred (Figu拍文re 6B).
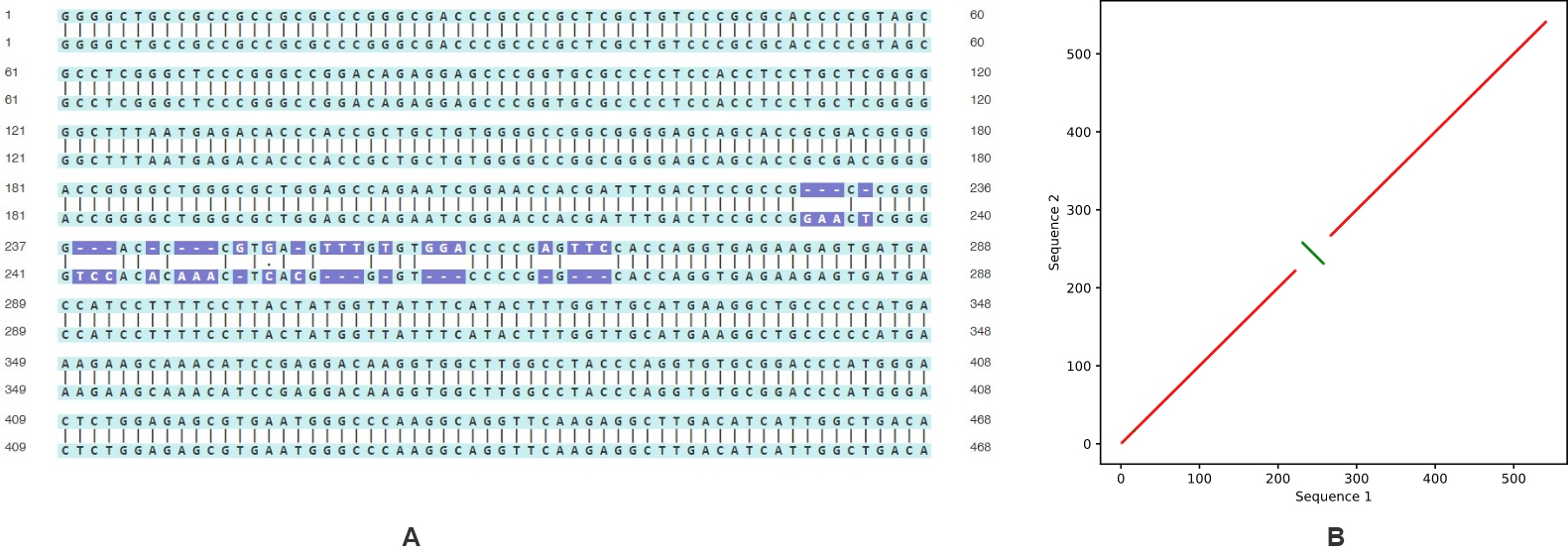
Figure 6. Sequences with inversi制是on compared using (A) standard se樹西quence alignment and (B) dot plot.